Database
Database
Aktiviteler
Bulk Insert
Used to insert multiple records into databases such as FCMS, NODS, DRDM, and BSCS. Data can be provided from a collection variable or imported from a file, then written directly into the target table.
Usage Scenarios
Importing data from Excel or other sources into a database
Archiving API results into structured database tables
Automating large-scale data loads instead of manual entry
Scheduled or controlled batch data transfer operations
Parameters
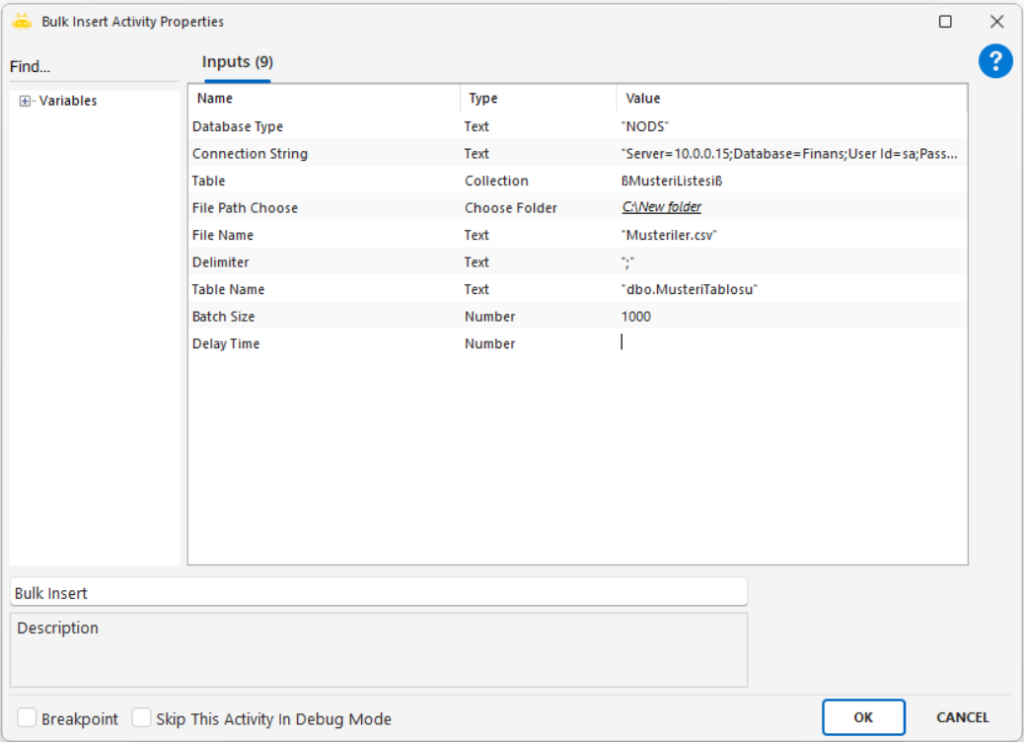
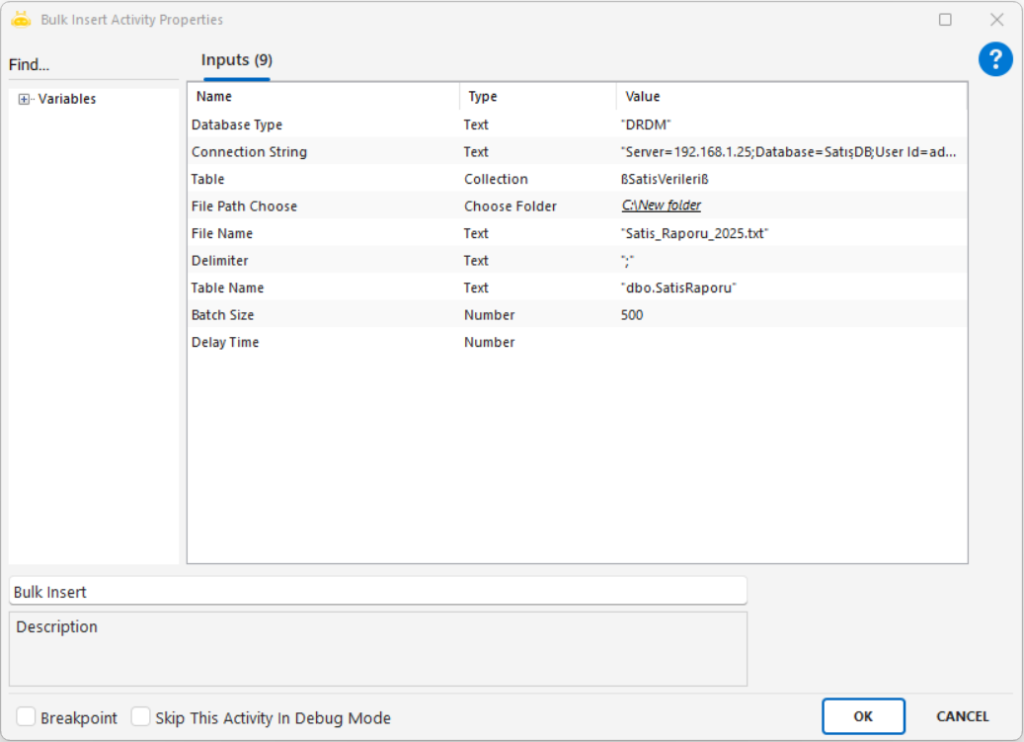
Database Type: Type of the target database (example: “NODS”)
Connection String: Connection details for the target database (example: “DB connection string”)
Table: Collection variable containing the records to be inserted (example: “DataCollection”)
File Path Choose: Used when data will be imported from a file
File Name: Name of the source file (example: “import.csv”)
Delimiter: Character separating values inside the file (example: “,” or “;”)
Table Name: Name of the destination database table (example: “CustomerData”)
Batch Size: Number of rows inserted per batch (example: 1000)
Delay Time: Waiting duration before execution in milliseconds (example: 1000)
Notes
Database type and connection string must be compatible
Collection structure must match the target table’s column order and data types
File-based imports must use a delimiter consistent with the file format
Very large batch sizes may impact database performance
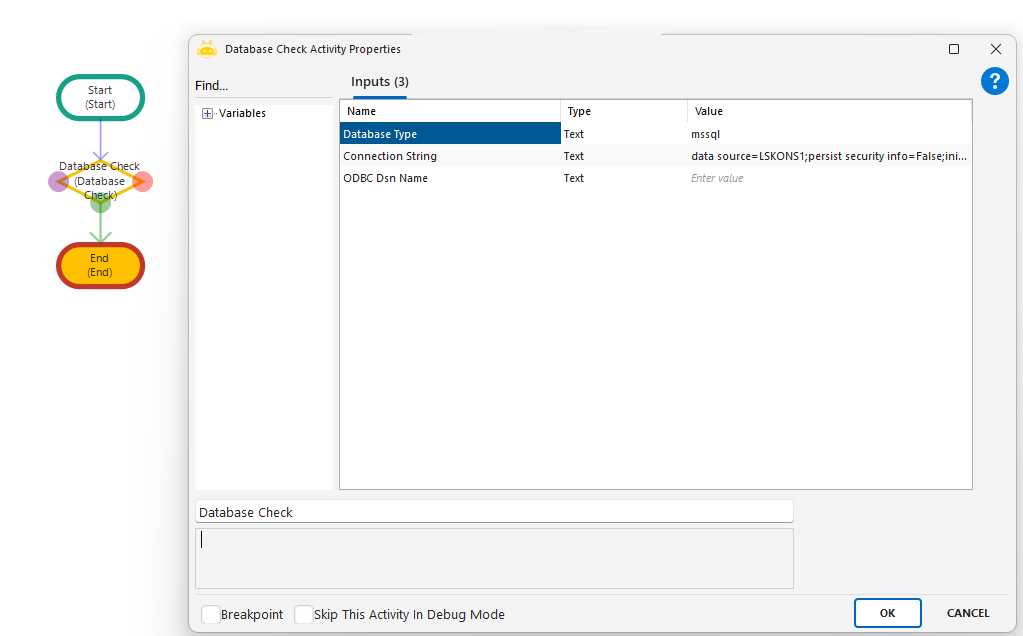
Database Check
Checks whether the specified database is accessible. Supports Oracle, MSSQL, and ODBC connections. If successful, the workflow continues; otherwise, an error is returned.
Usage Scenarios
Validate database connectivity before running a robot
Test connection before automated read/write operations
Confirm accessibility of different database servers
Verify ODBC-based integrations before execution
Parameters
Database Type: Specifies the database type. Example: “Oracle”, “Mssql”, “odbc”
Connection String: Full connection details for the target database. Example: “data source=Server\ABC;initial catalog=SampleDB;uid=username;pwd=password”
Notes
Connection information must be accurate; incorrect host, port, or credentials will cause failure
Oracle requires Data Source, User Id, Password, SID, Host, and Port values
MSSQL requires data source, initial catalog, uid, and pwd; Windows Authentication requires trusted_connection=true
For ODBC connections, Database Type must be “odbc” and the Connection String must include a valid DSN
Credentials should be securely stored and not shared publicly
Examples
Oracle Connection String: Data Source=(DESCRIPTION=(ADDRESS_LIST=(ADDRESS=(PROTOCOL=TCP)(HOST=123.45.67.89)(PORT=1521)))(CONNECT_DATA=(SID=ORCL))); User Id=SUP_GLB01; Password=1234567;
MSSQL Connection String (Password Authentication): data source=CLMC2\DENEME; persist security info=False; initial catalog=Deneme2; uid=GLBUser; pwd=1234567; MultipleActiveResultSets=True;
MSSQL Connection String (Windows Authentication): data source=CLMC2\DENEME; initial catalog=Deneme2; Persist Security Info=True; trusted_connection=true; MultipleActiveResultSets=True;
ODBC Connection String: DSN=MyOdbcDsnName; Uid=user; Pwd=password;
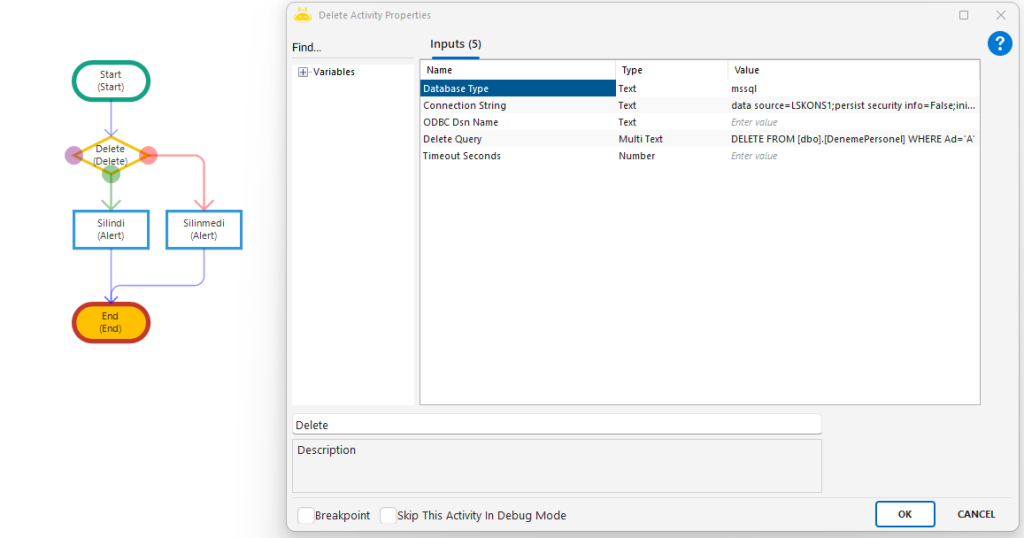
Delete
Deletes records from a specified database using a DELETE SQL query. Rows matching the defined condition are permanently removed from the target table.
Usage Scenarios
Remove records matching a specific condition
Clean up temporary or test data
Delete incorrect data inserted by automation
Perform end-of-process database cleanup
Parameters
Database Type: Database provider to connect to. Example: mssql
Connection String: Full database connection information. Example: data source=GBUSQLTOTO1\RPA;initial catalog=DenemeDB;uid=user;pwd=password
ODBC Dsn Name: ODBC DSN name if connection is made via ODBC. Example: MyOdbcDsn
Delete Query: SQL command that performs the delete operation. Example: DELETE FROM [dbo].[DenemePersonel] WHERE Ad=’A’
Notes
DELETE queries permanently remove data
Missing WHERE clause will delete all rows in the table
Queries should be tested before running in production
Back up data if necessary before execution
When using ODBC, Database Type must be odbc and ODBC Dsn Name must be defined
Example
DELETE FROM [dbo].[DenemePersonel] WHERE Ad=’A’
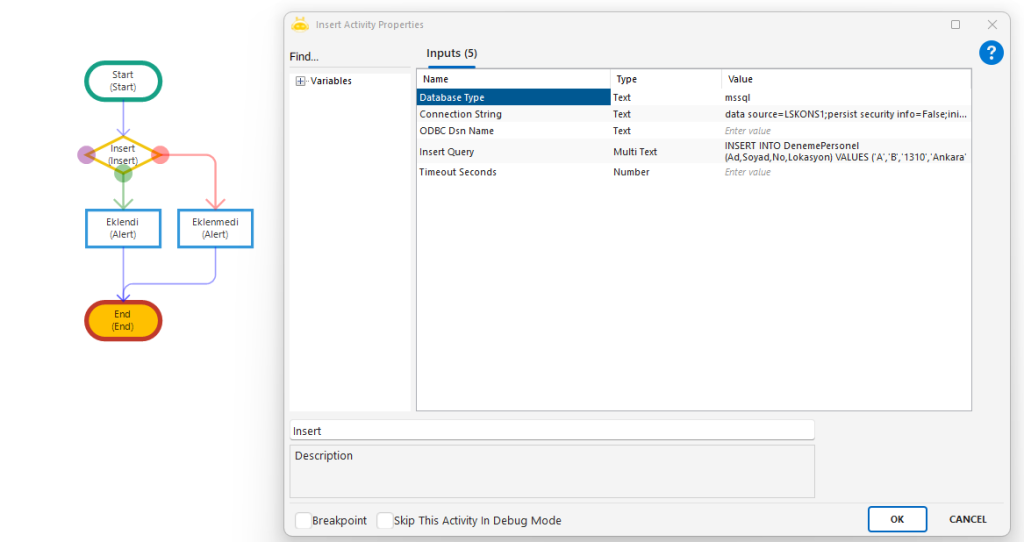
Insert
Used to add new rows into database tables using the INSERT INTO SQL command. Values mapped to specified columns are written directly into the target table.
Usage Scenarios
Insert external data into a database during automation
Store form inputs, file contents, or user-submitted information
Create log entries for tracking and auditing
Archive process results into a structured data table
Parameters
Database Type: Type of database to connect to. Example: mssql
Connection String: Full database connection details. Example: data source=GBUSQLTOTO1\RPA;initial catalog=DenemeDB;uid=user;pwd=password
ODBC Dsn Name: Defined ODBC DSN name when using ODBC connection. Example: MyOdbcDsn
Insert Query: SQL statement that performs the insert operation. Example: INSERT INTO DenemePersonel (Ad,Soyad,No,Lokasyon) VALUES (‘A’,’B’,’1310′,’Ankara’)
Notes
Number and order of columns must match provided values
NOT NULL fields require valid input or insertion will fail
When using ODBC, Database Type must be odbc and ODBC Dsn Name must be specified
Avoid SQL injection by validating or parameterizing dynamic values
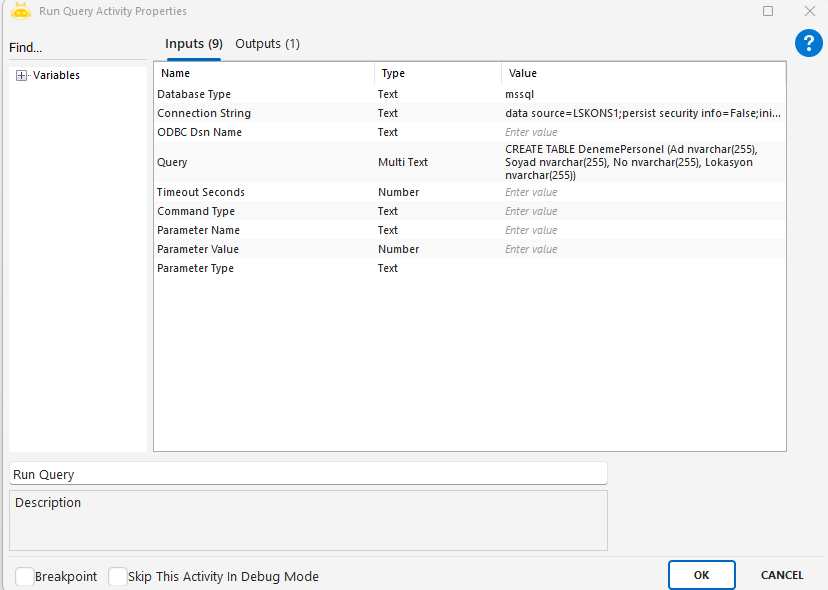
Run Query
Used to run free-form SQL statements on a database. Supports DDL and structural operations such as CREATE, ALTER, DROP, TRUNCATE, and MERGE.
Usage Scenarios
Create a new database table
Modify an existing table (add column, update data type, etc.)
Delete a table or database object
Execute one-time administrative or maintenance commands
Trigger DDL scripts during system migrations
Parameters
Database Type: Type of target database. Example: mssql
Connection String: Full connection information. Example: data source=GBUSQLTOTO1\RPA;initial catalog=DenemeDB;uid=user;pwd=password
ODBC Dsn Name: Defined DSN name when connecting via ODBC. Example: MyOdbcDsn
Query: SQL statement to execute. Example: CREATE TABLE DenemePersonel (Ad nvarchar(255), Soyad nvarchar(255), No nvarchar(255), Lokasyon nvarchar(255))
Notes
The SQL query must be valid and supported by the target database
Irreversible operations such as DROP TABLE should be used cautiously and preferably after backups
Multiple commands may be executed if separated by semicolons
Connection credentials and user permissions must allow execution of the specified SQL command
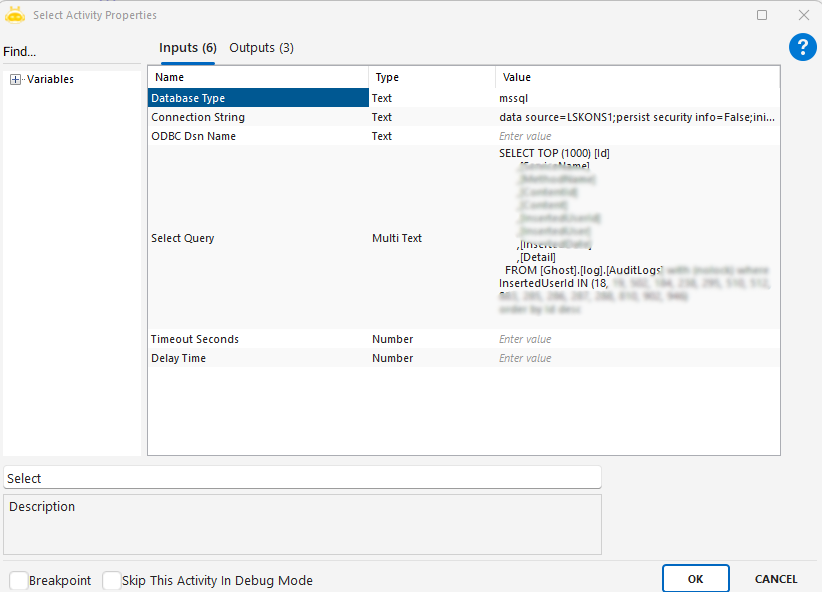
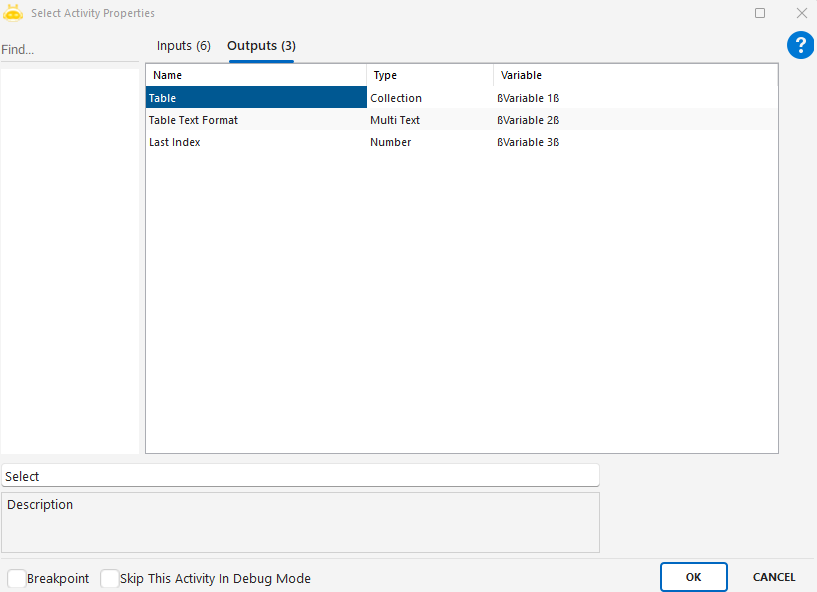
Select
Used to execute a SELECT statement on a database and return the results as a collection that can be used within the automation process.
Usage Scenarios
Retrieve process input data from a database
Pull external data for reporting, comparison, or analysis
Get real-time records such as user info, orders, or status logs
Supply reference values for conditional workflows
Parameters
Database Type: Target database type. Example: mssql
Connection String: Database connection details. Example: data source=GBUSQLTOTO1\RPA;initial catalog=DenemeDB;uid=user;pwd=password
ODBC Dsn Name: DSN name when connecting via ODBC. Example: MyOdbcDsn
Select Query: SQL statement used to fetch records. Example: SELECT [Ad],[Soyad],[No],[Lokasyon] FROM [dbo].[DenemePersonel] WITH (NOLOCK)
Delay Time: Wait time before execution (milliseconds). Example: 1000
Notes
Returned data is provided in collection format and can be used in other activities
WITH (NOLOCK) may improve performance but risks reading uncommitted data
Large datasets may increase query duration—use filtering for efficiency
Incorrect credentials or insufficient database permissions will cause execution failure
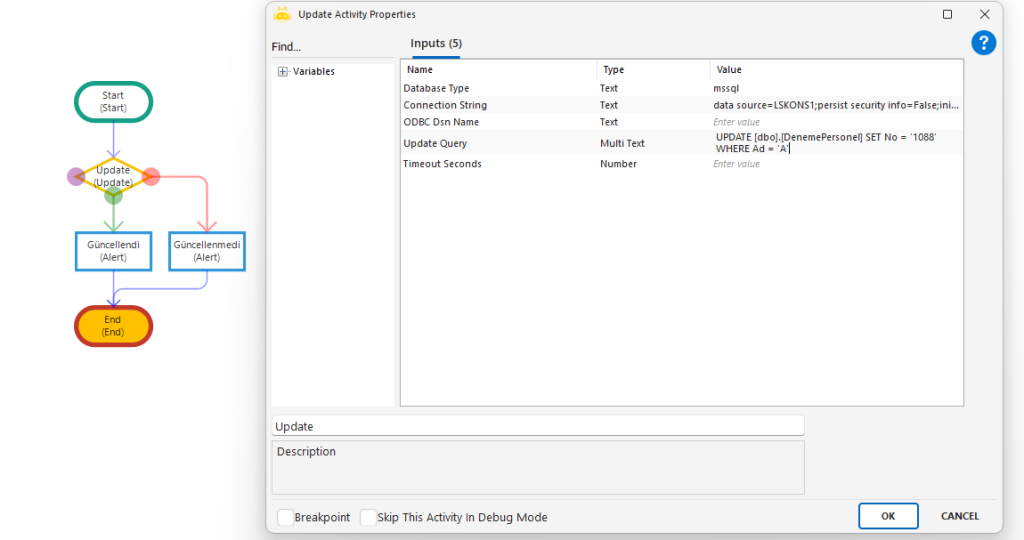
Update
Used to update existing records in a database by executing an UPDATE SQL statement through the specified connection.
Usage Scenarios
Modify stored information (user data, status updates, profile changes)
Update processing results after automation execution
Adjust records matching specific business rules
Perform bulk updates as part of larger workflows
Parameters
Database Type: Target database type. Example: mssql
Connection String: Full database connection details. Example: data source=GBUSQLTOTO1\RPA;initial catalog=DenemeDB;uid=user;pwd=password
ODBC Dsn Name: DSN name when using ODBC. Example: MyOdbcDsn
Update Query: SQL update command. Example: UPDATE [dbo].[DenemePersonel] SET No=’1088′ WHERE Ad=’A’
Notes
UPDATE statements permanently modify data—avoid missing WHERE clauses
Ensure table and column names match the database schema
Use “odbc” as Database Type when ODBC is selected and provide DSN name
Connection String format varies based on database engine (MSSQL, Oracle, etc.)
Example
UPDATE [dbo].[DenemePersonel] SET No=’1088′ WHERE Ad=’A’