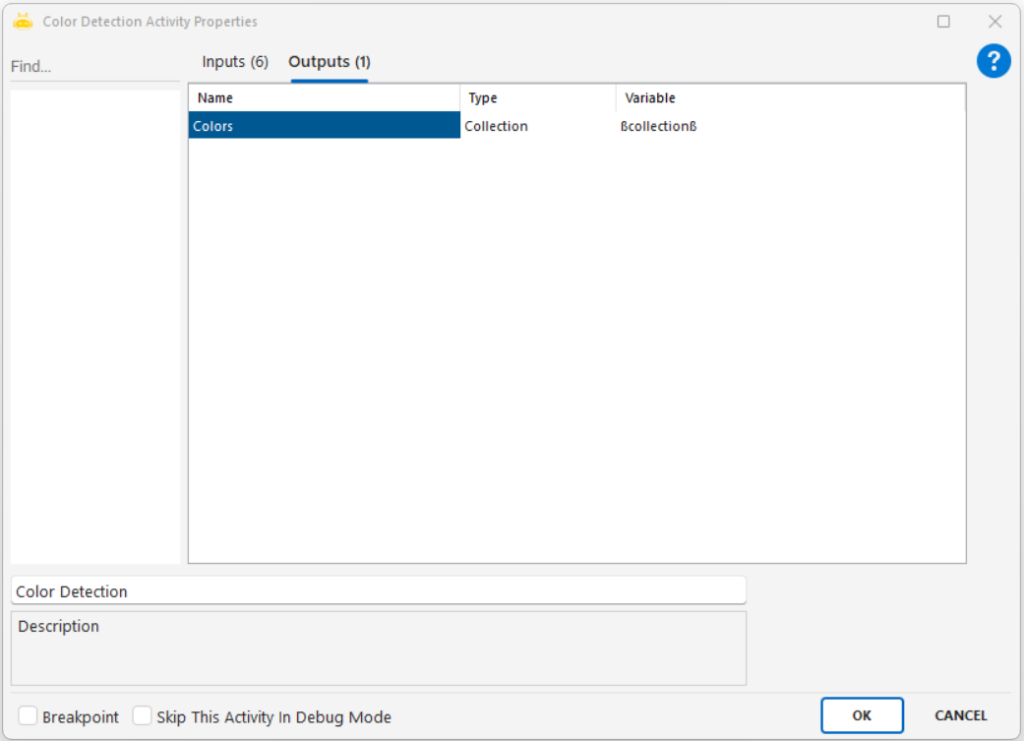
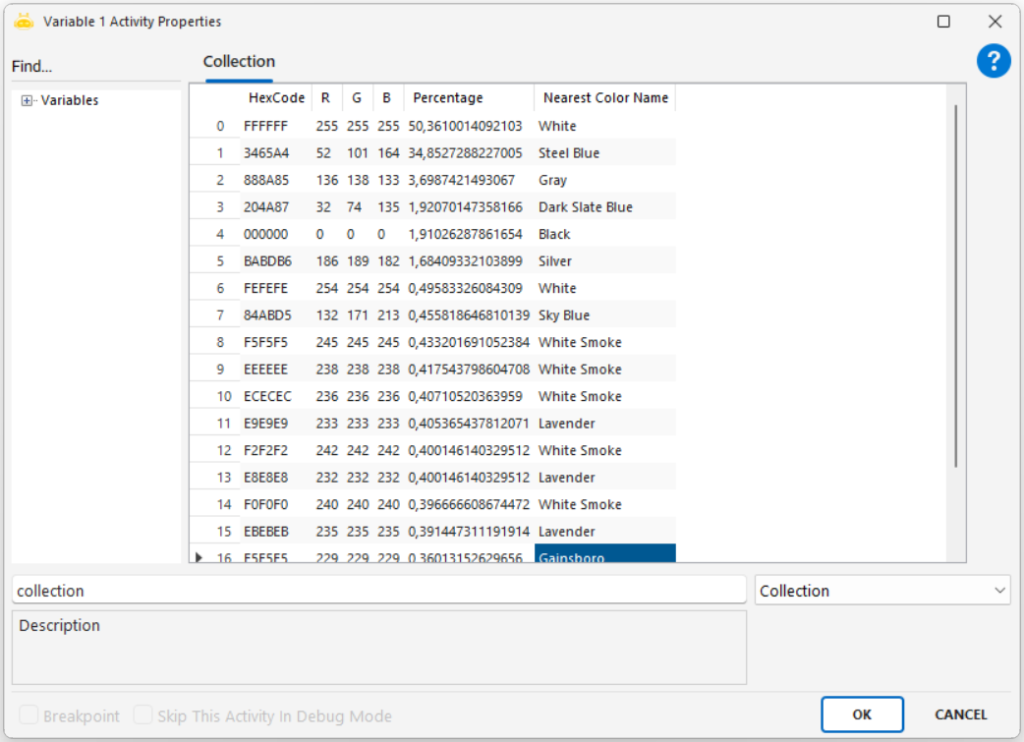
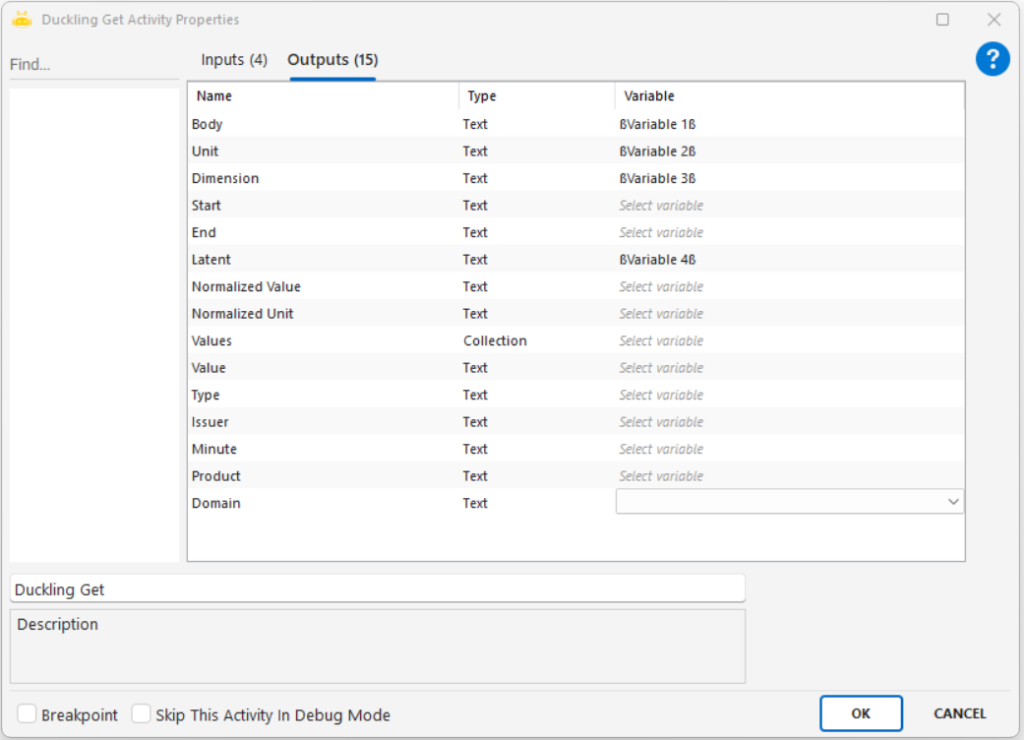
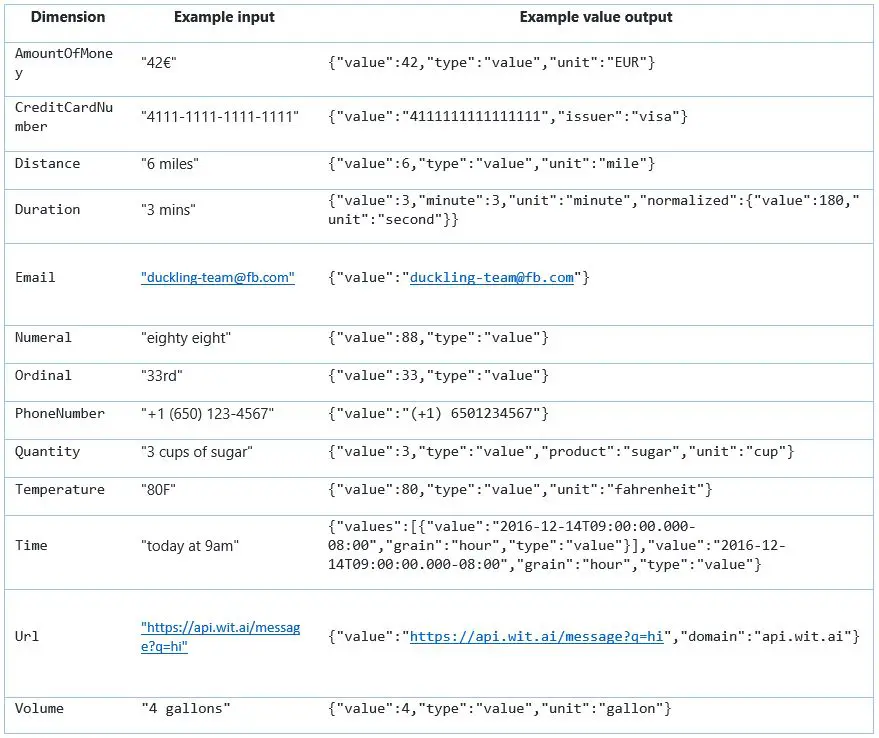
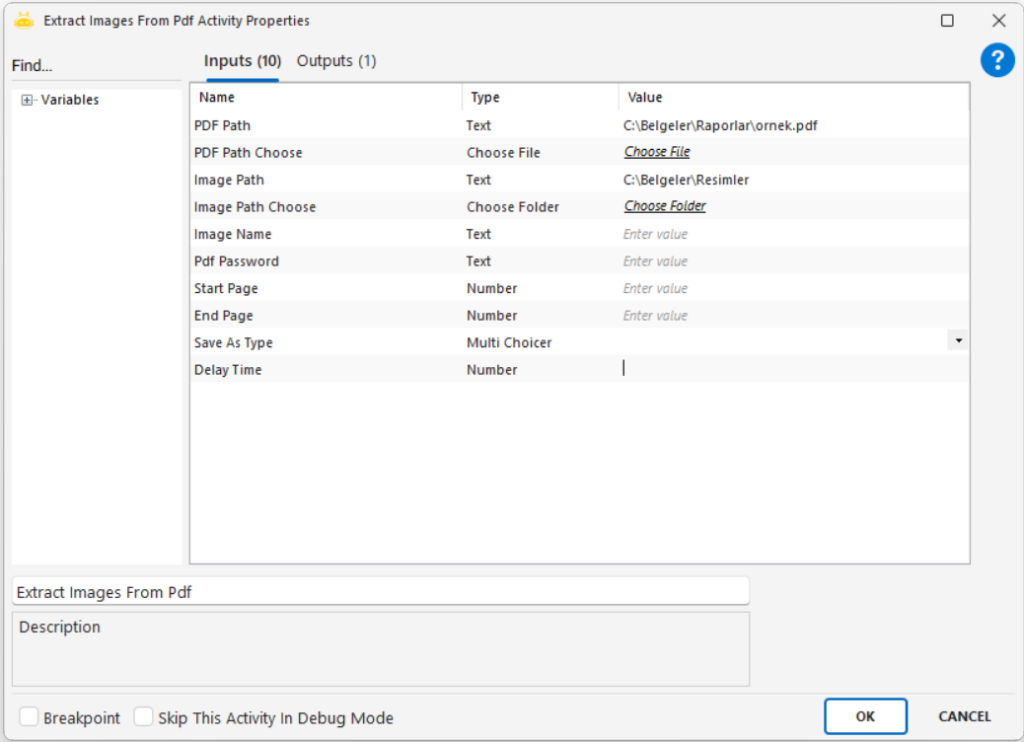
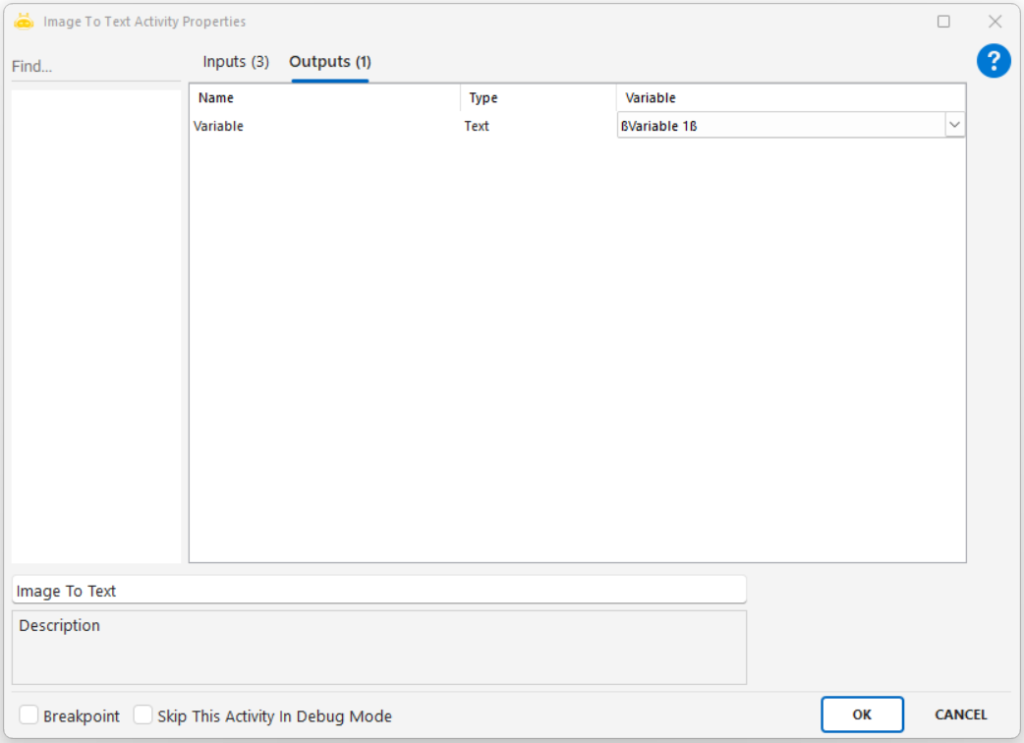
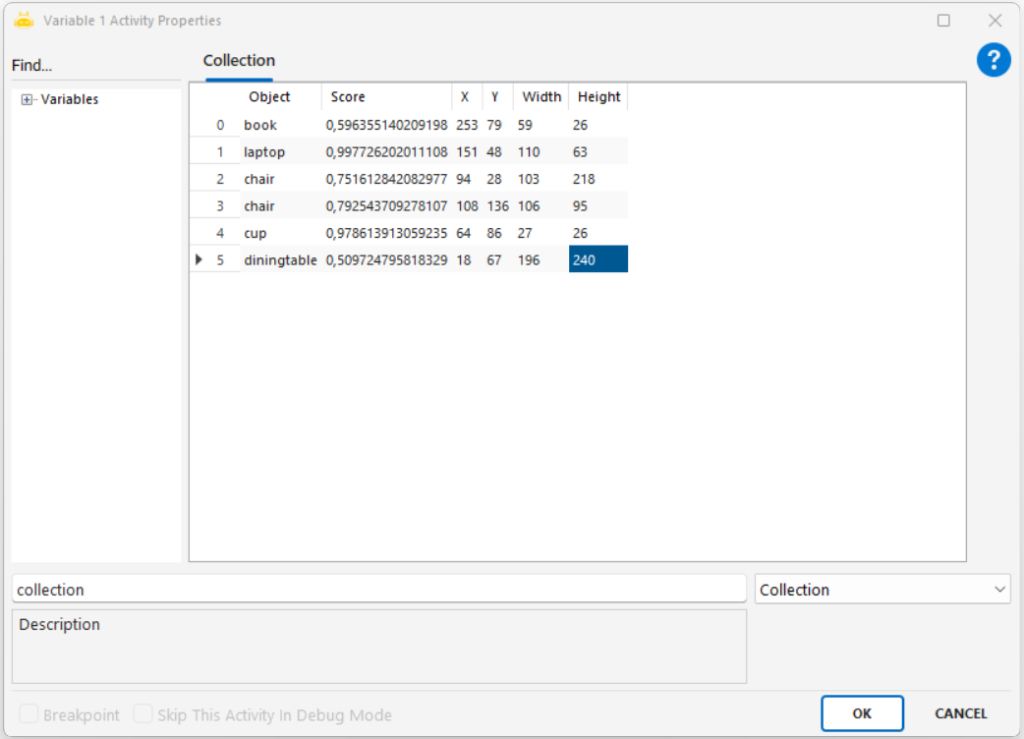
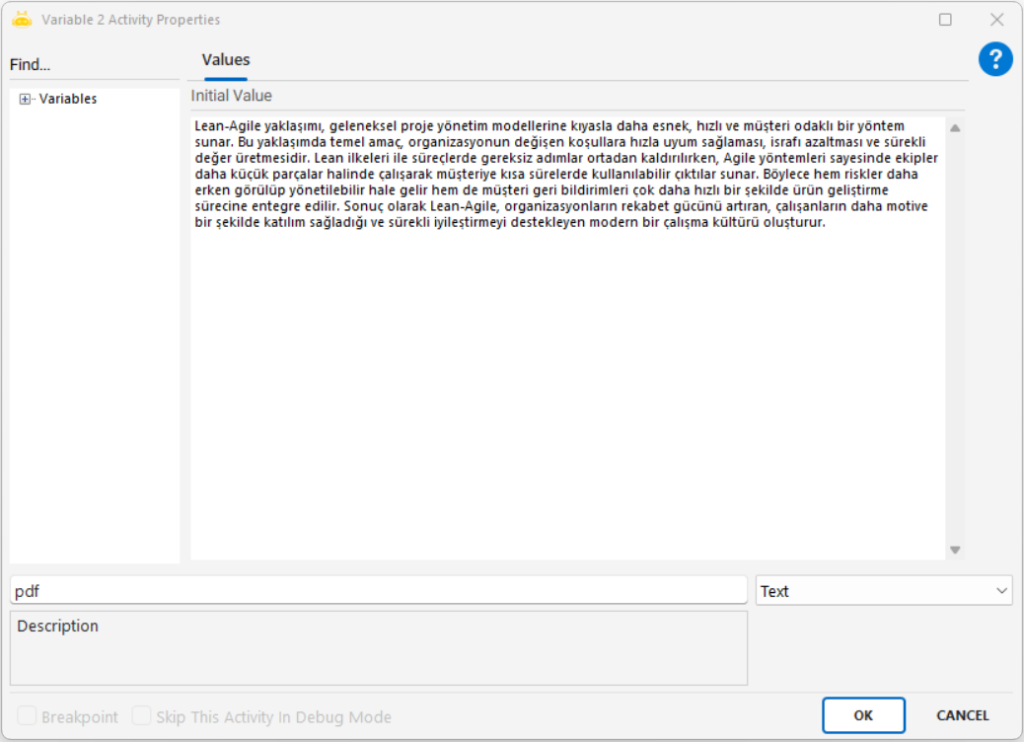
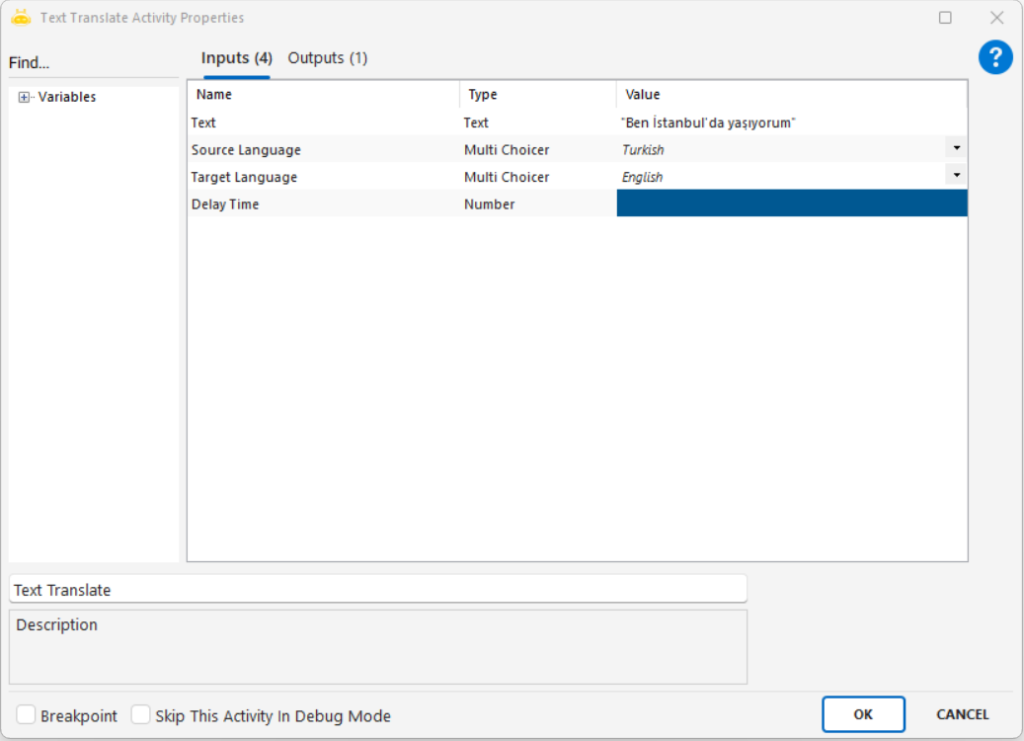
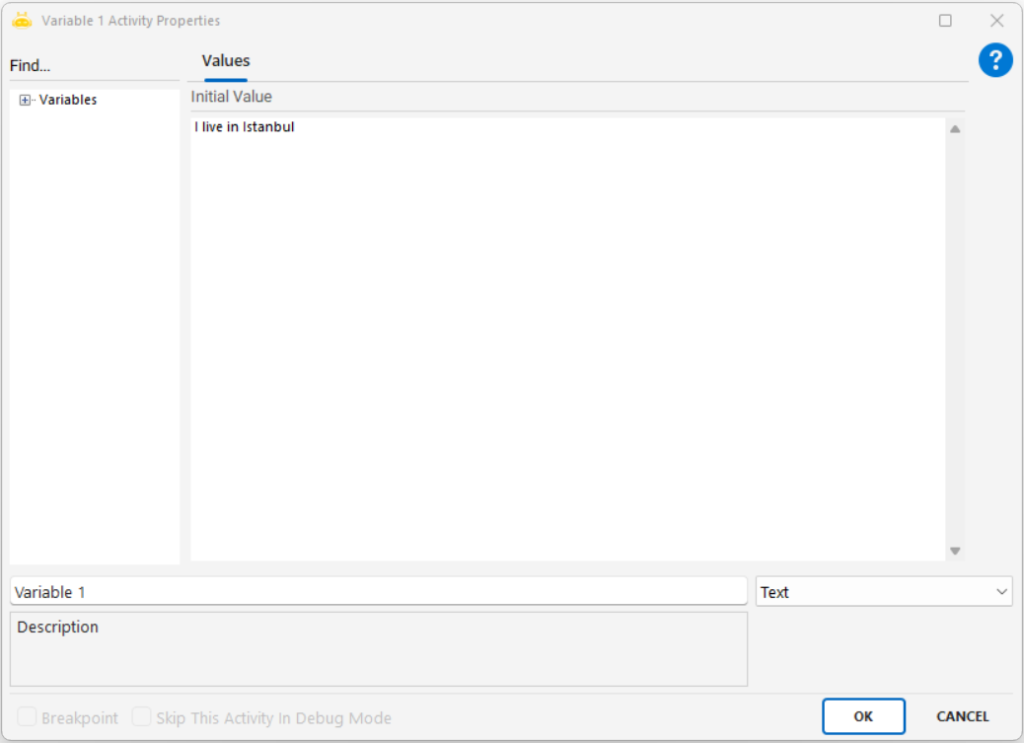
Extracts textual or numeric information from an image file using Optical Character Recognition (OCR) and outputs the result into a variable.
Usage Scenarios
Extracting text from invoices, receipts, or forms
Converting written content in images into digital data
Reading identifiers such as invoice numbers or national IDs
Capturing text from screenshots
Digitizing user inputs on image-based forms
Parameters
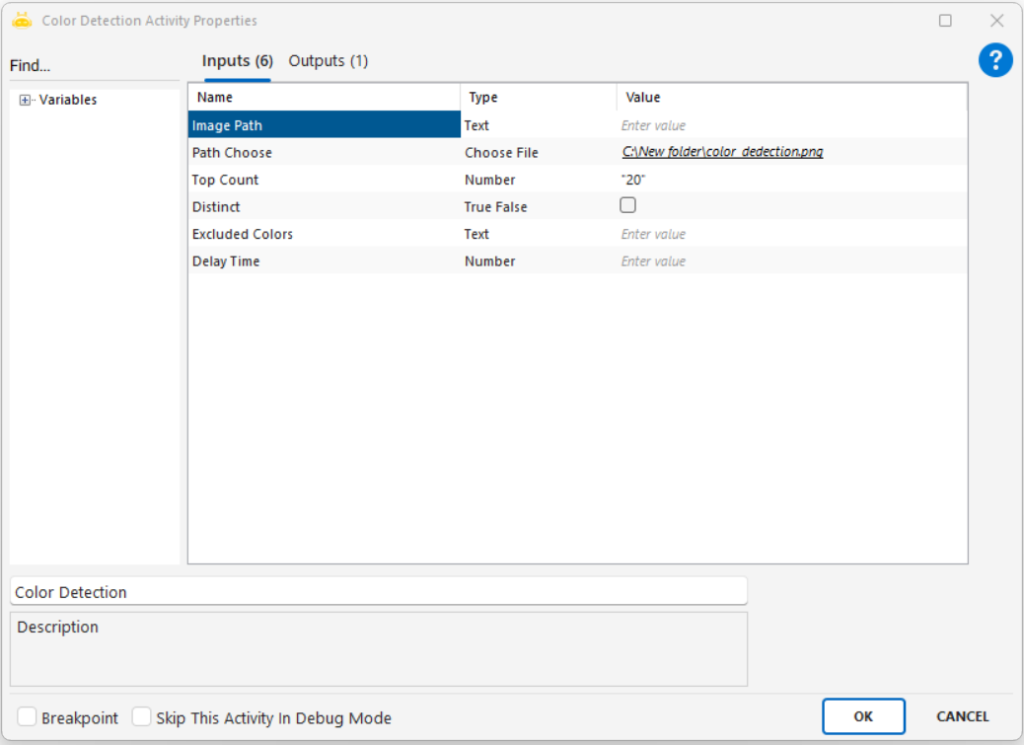
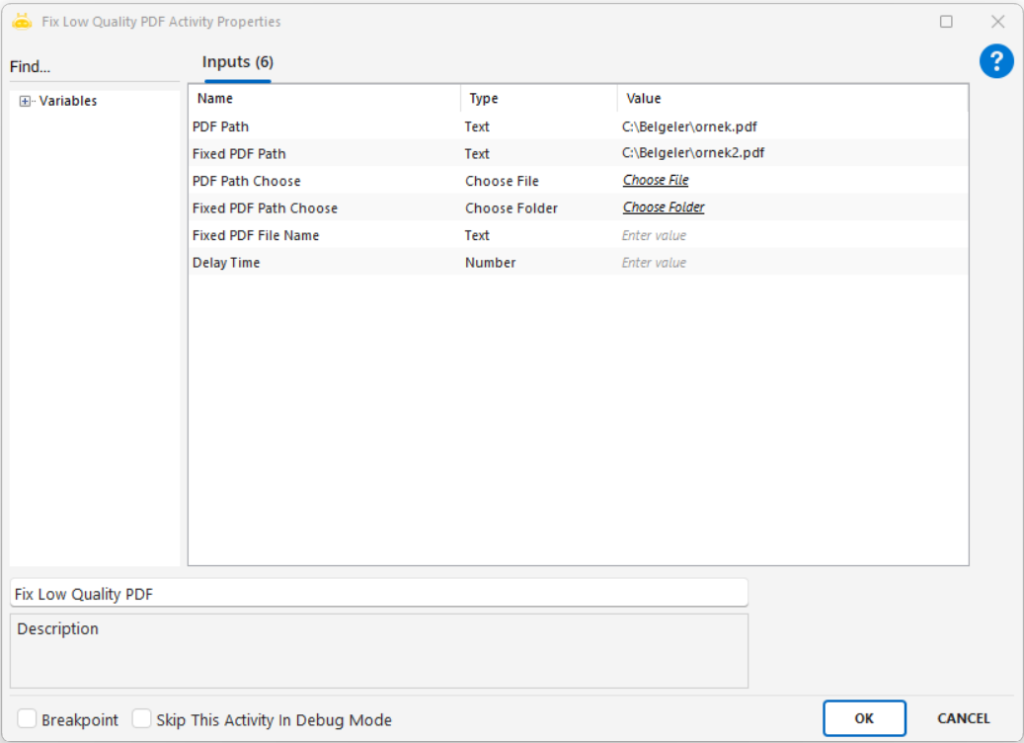
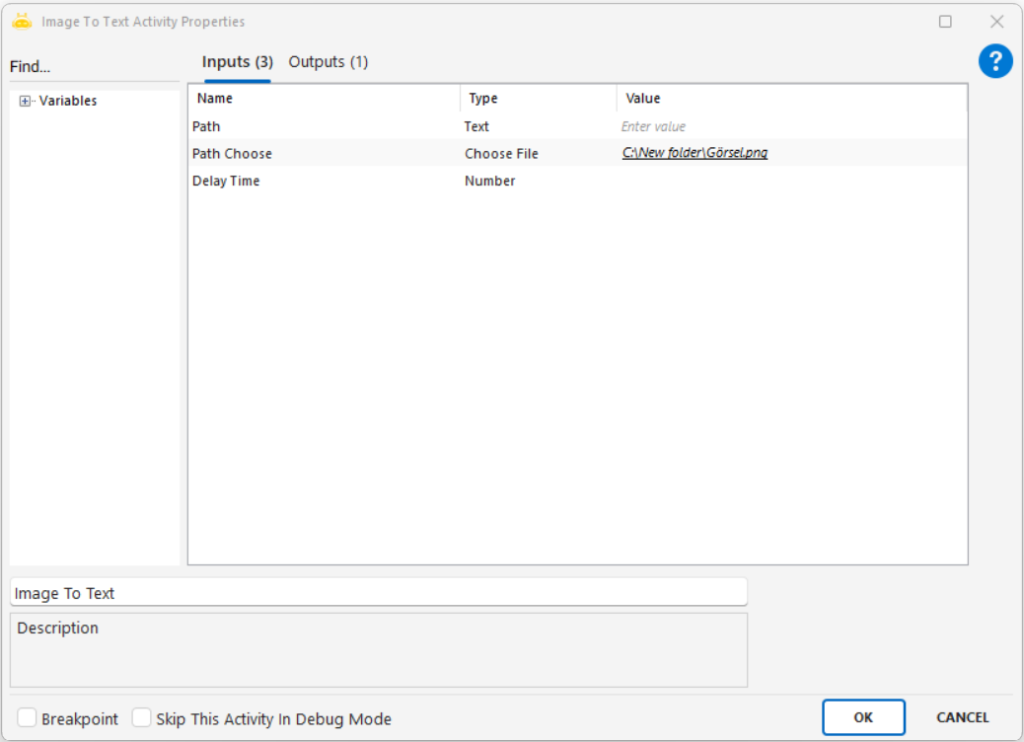
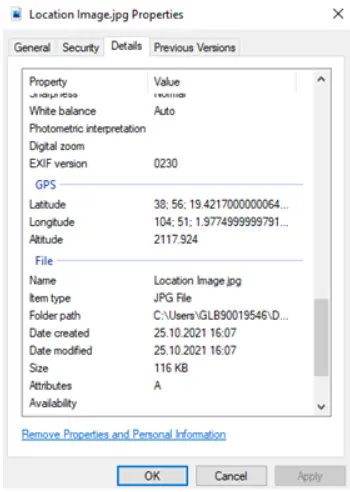
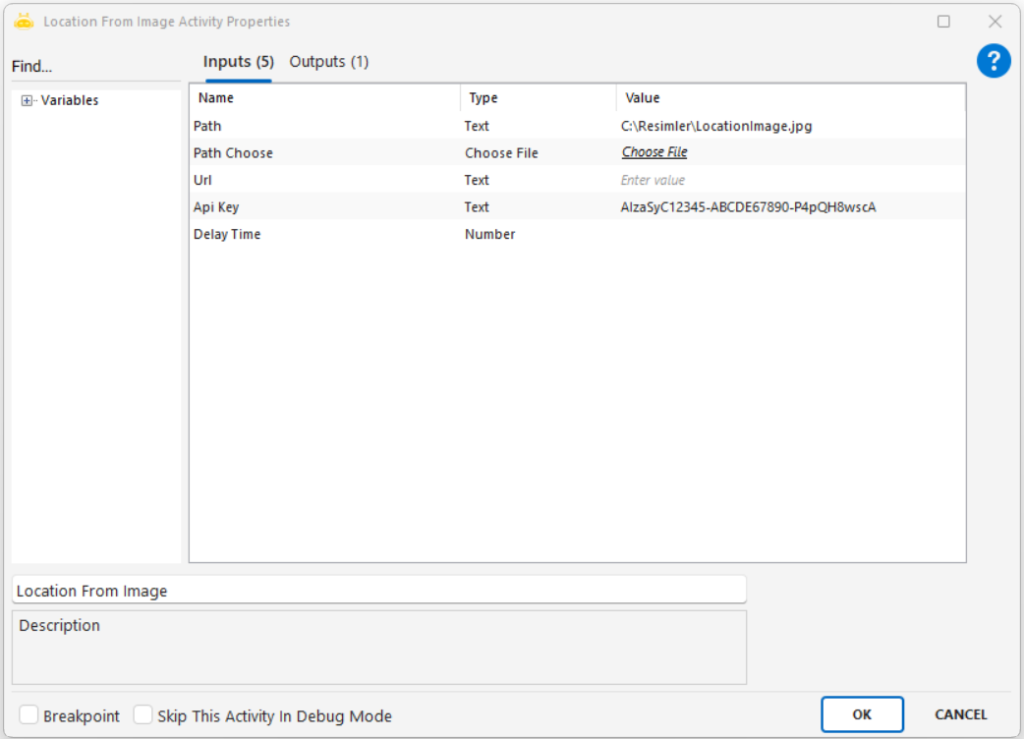
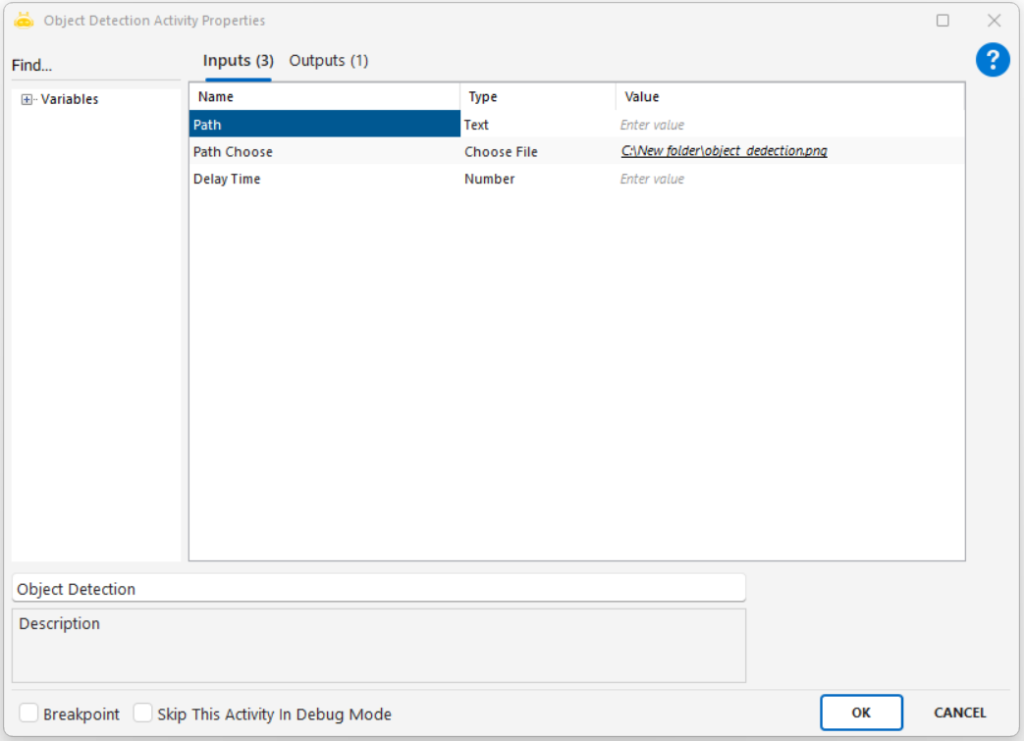
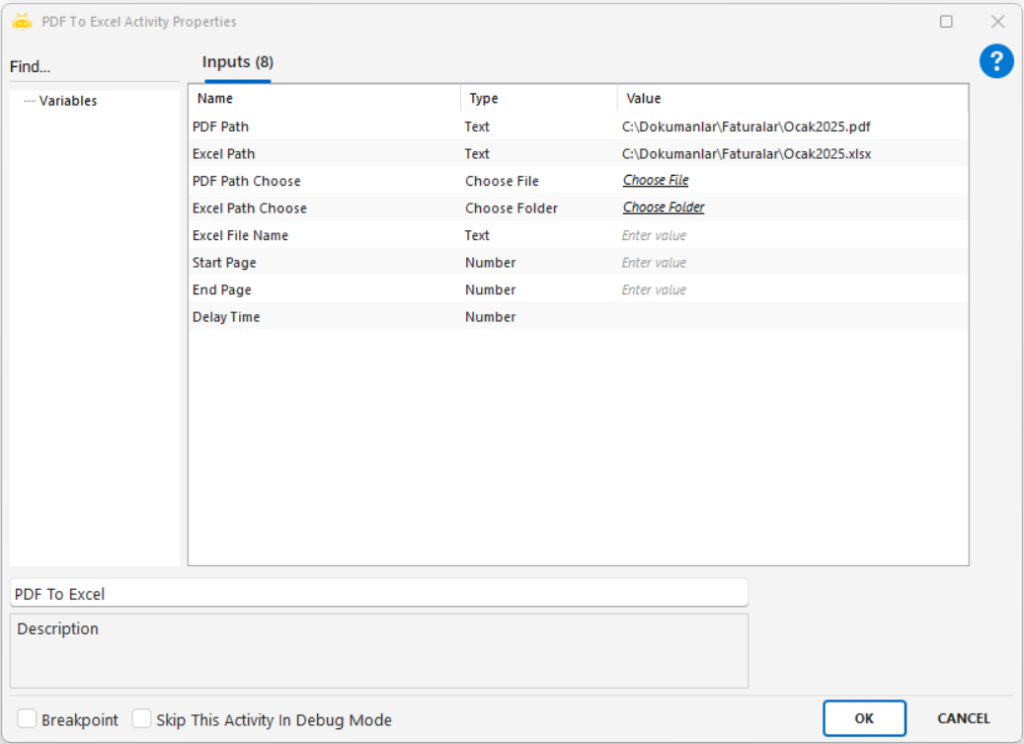
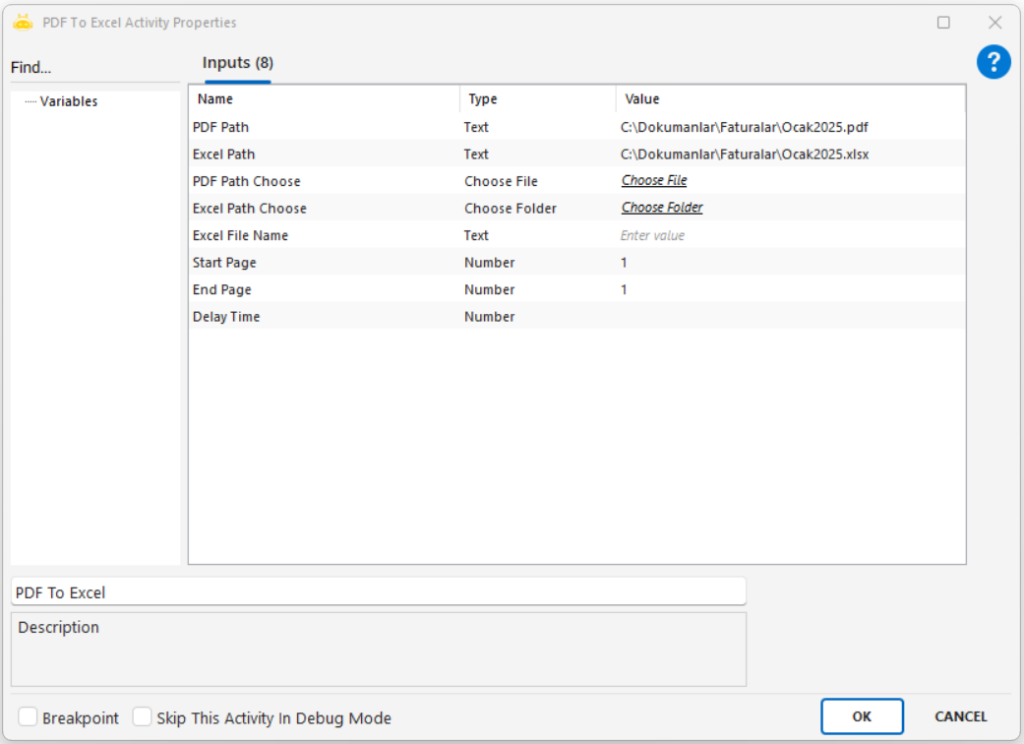
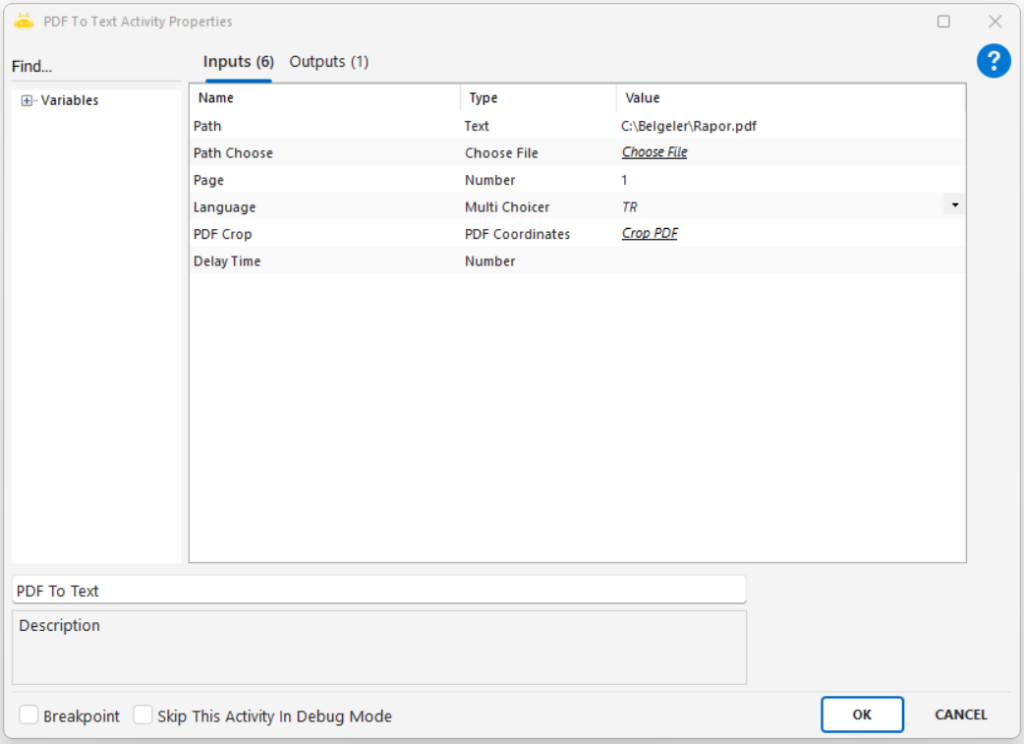
Path: Full file path of the image to be processed (e.g., “C:\New folder\sample.png”)
Path Choose: Selects the image file through the UI
Notes
The image must be clear and readable; blurry images reduce OCR accuracy
Font style, size, and contrast affect recognition quality
Large or high-resolution images may increase processing time
Only one of Path or Path Choose needs to be provided